A re you looking to get HTTPS free to secure your blog, protect your visitors, and rank higher in search results?
You’re in luck—I’m going to walk you through the process of how to get HTTPS free in the form of an SSL certificate step-by-step.
If you run a blog or website you’ve probably heard about SSL certificates and the idea of moving your domain from the old HTTP to the secure HTTPS version. It’s a very important topic!
In fact, this is something that will affect the security, performance and even the search engine rankings of your blog.
Today I’ve got a huge post filled with information about how to get a free SSL certificate and HTTPS for your blog, including why people are moving, what Google has been saying about it, and even step-by-step instructions on how to get it done for free.
This is a pretty complicated topic and so we’ve gone into lots of detail to try and make it as pain-free as possible. Have a read and jump in the comments if you’re still unsure.
Before we jump in, here’s a table of contents so you can skip ahead to the section you’re interested in about getting an ssl for free.
I’m starting off by answering some common questions first, but you can just click here to skip to the tutorial if you prefer.
In This Guide:
Ready? Let’s begin!
What Is an SSL Certificate?
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer, and it’s basically website security technology that secures any data exchanged between your website and your visitors’ computers.
What data does it secure, exactly?
Whenever someone visits your website, information is passed back and forth between their browser and your website. That information can include sensitive data like:
- Addresses
- Credit card numbers
- Email addresses
- Passwords
- …and more
That means you’ll definitely need an SSL certificate if you have:
- A membership site that required users to login
- An online store that required users to pay for goods or services
What about blogs or other types of websites?
Well, Google recommends that all websites use SSL to protect your visitors, no matter what kind of website you have.
They even recognize secure sites by rewarding them with better search engine rankings, so you’ll get more traffic.
How Does an SSL Certificate Keep Information Secure?
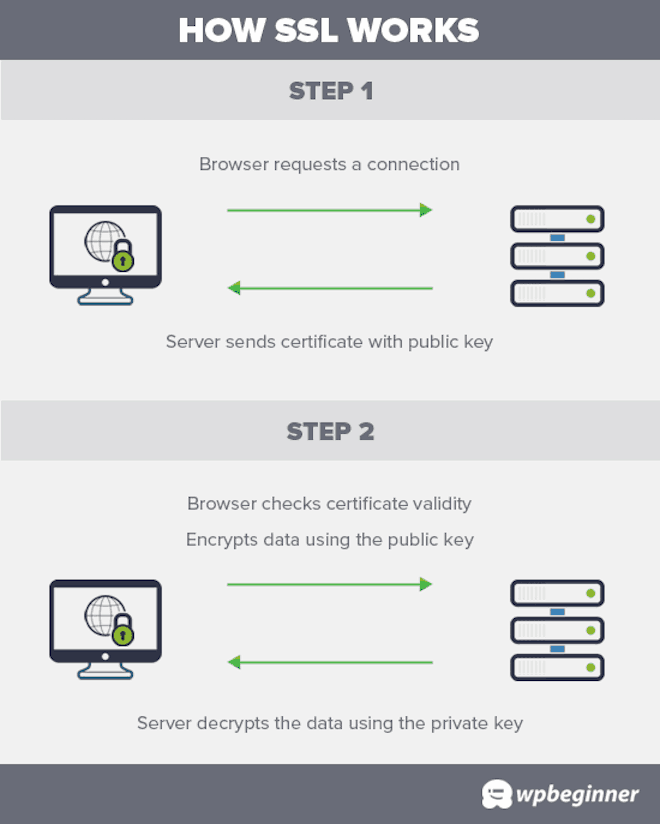
An SSL certificate is a digital computer file (or a small piece of code) that enables encryption.
Just like you need a key to lock and unlock a door, encryption uses keys to lock and unlock information. And unless you have the right key, you can’t access the information.
Each SSL session consists of two keys:
- The public key is used to encrypt (scramble) the information.
- The private key is used to decrypt (unscramble) the information and restore it to its original format so that it can be read.
Here’s how the SSL encryption process works:
How Do I Know if a Site Has a Valid SSL Certificate?
Major browsers like Chrome, Firefox, and Safari all display a padlock icon for sites that already have an SSL certificate, reassuring users of their security. A website that has the extra layer of security of a valid SSL certificate also displays HTTPS (Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol) before the website’s URL in the address bar:
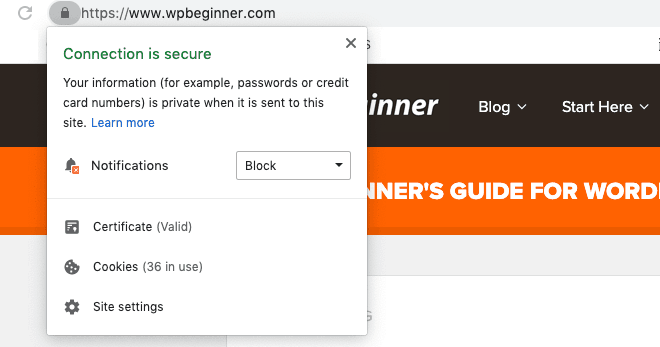
You can click the padlock to display information about the certificate.
What about for sites that don’t have an SSL certificate installed?
If you’re using the Google Chrome browser like over 70% of internet users, you’ll see an alarming warning message before you can even access the website.
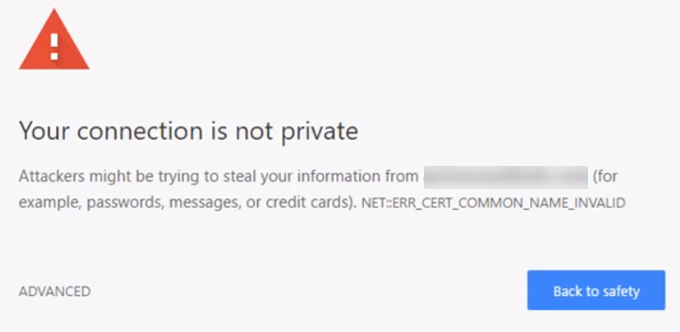
If you visit the site anyway, you’ll see the warning “Not Secure” and HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) before the website address:
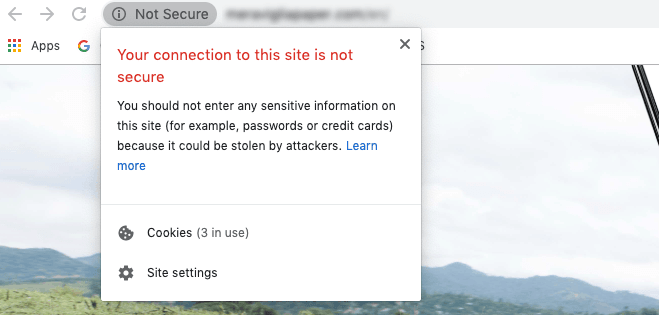
If you don’t want to scare off your potential website visitors, you’ll need to make your site secure!
How Much Does an SSL Certificate Cost?
SSL certificates vary in price depending on:
- The type of SSL Certificate
- The number of the domains and subdomains
- The period they cover
- The brand (Certificate Authority)
For example, leading domain registrar Domain.com offers 3 SSL certificates ranging from $35 – $269 a year.
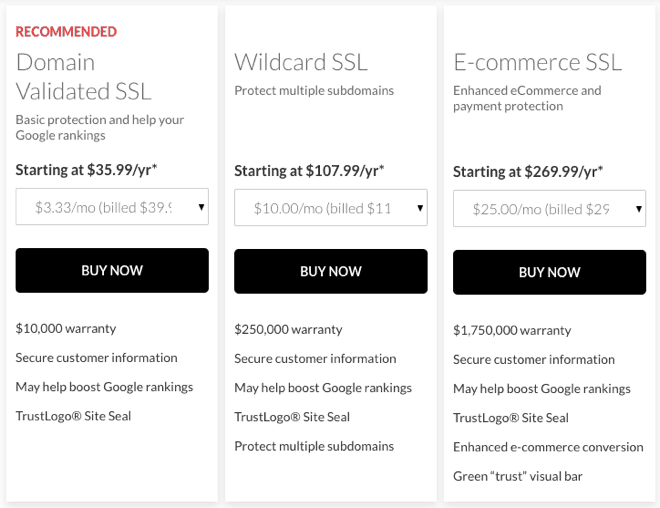
But for most bloggers, these prices may seem excessive, and in truth, you don’t need such a high layer of security.
Thankfully, there’s a free SSL certificate provided by Let’s Encrypt, that will suit most bloggers.
How Can I Get a Free SSL Certificate?

Let’s Encrypt is a non-profit Certificate Authority that offer free SSL certificates because they want to create a more secure and privacy-respecting web.
Since launching the project, many industry leaders like WPBeginner, Google Chrome, Facebook, Shopify, and Automattic have decided to sponsor them.
Although it’s easy to get a free Let’s Encrypt SSL certificate, it’s not so easy to install one.
But now, many of the best WordPress hosting companies offer Let’s Encrypt to secure your website and take care of the SSL certificate installation.
Many hosting provider options offer a free SSL certificate with their hosting plans.
We recommend Bluehost because they also offer a free domain (web address), great support, and reasonable prices for bloggers and other website owners.
Get a Free SSL Certificate With Bluehost!
Bluehost offers 99.99% uptime and lightning-fast loading times, plus a free domain and free SSL certificate with their shared hosting.
Get started with bluehost todayWith Bluehost your free SSL certificate should install and activate itself when you signup. For existing users, you’ll find the free SSL certificate by visiting My Sites, moving along to the Security tab, and switching on the Free SSL Certificate for your website:
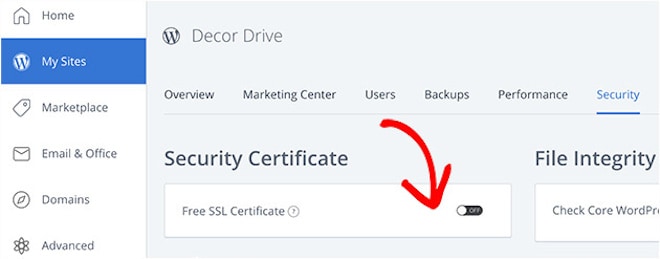
Other hosting companies will work similarly, but you can always check with the respective support team if you have any questions.
How to Install a Free SSL Certificate in WordPress
After you’ve switched on your free SSL Certificate in your web hosting dashboard, you’ll need to set up WordPress to start using HTTPS instead of HTTP in all your URLs.
Adding an SSL certificate manually to protect your website can be a bit tricky, so the easiest way to do this is by installing and activating the Really Simple SSL plugin:

For more details, see our step-by-step guide on how to install a WordPress plugin.
Once you’ve installed and activated the plugin, it will run some initial checks and configuration in the background.
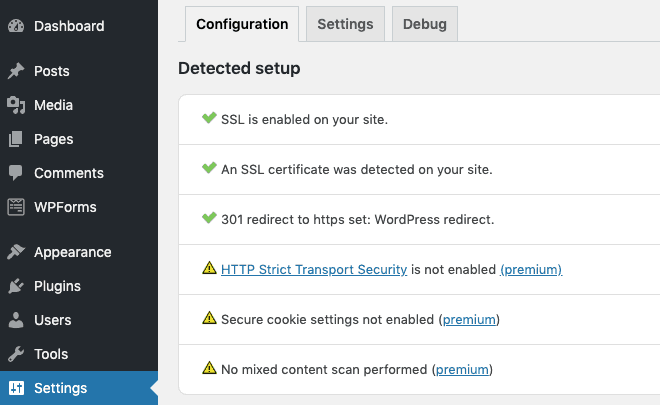
You’ll notice the successful green check marks against the top items. For the remaining items, you’ll need to install the premium version of the plugin.
Really Simple SSL Pro is an addon to Really Simple SSL, so you don’t have to deactivate the free version. The premium version makes further checks and locates what’s known as mixed content.
Note: Mixed content occurs when some of your content is HTTPS, while some remains as HTTP. Unfortunately, some theme and plugin files have poor coding, which keeps the content as HTTP rather than allowing it to switch to HTTPS.
If you have mixed content, then your site won’t display the reassuring padlock symbol you expect to see with an SSL certificate. Instead, visitors see an information icon, and a message explaining that the site is not fully secure:
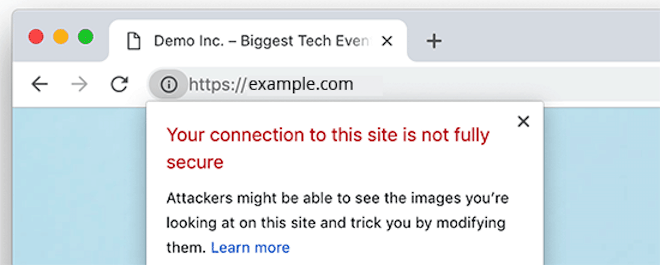
Really Simple SSL Pro detects the source of the mixed content that couldn’t be fixed automatically, and lets you fix it manually. The Pro version also provides further advanced options to:
- Enable HTTP Strict Transport Security
- Configure your site for the HSTS preload list
The Really Simple SSL plugin makes it easy to set up your free SSL certificate in WordPress. And that’s why we recommend it to all beginners.
But if you’re feeling more adventurous, then you can check out this tutorial, which shows you how to switch WordPress from HTTP to HTTPS with and without the plugin.
Two more settings to configure:
Google treats the HTTP and HTTPS versions of your website separately, so you’ll need to update Google Search Console and Google Analytics when you migrate your site from HTTP to HTTPS:
- Add the new HTTPS property to Google Search Console.
- Change the protocol of your website from HTTP to HTTPS in Google Analytics.
SSL Certificate FAQs
Whether you’re new to SSL certificates or looking to deepen your understanding, this FAQ section aims to answer the most common questions.
How can a Wildcard SSL Certificate help when managing multiple domains?
A Wildcard SSL Certificate allows you to secure all subdomains of a domain with a single certificate, reducing administrative tasks and simplifying security management.
How do I set up a Wildcard SSL Certificate?
Setting up a Wildcard Certificate involves generating a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) and completing the domain validation process to verify ownership.
Why is it important to renew SSL certificates regularly?
Regularly renewing your SSL certificate ensures continuous protection of your website and prevents certificate expiration, which can disrupt security and user trust. The renewal process involves verifying your domain ownership again and updating the certificate on your server. Your hosting provider may automatically renew your certificate for you.
What does forcing HTTPS mean, and why should I do it?
Forcing HTTPS means configuring your server to redirect all HTTP traffic to HTTPS, ensuring all data exchanges between your site and visitors are encrypted, enhancing security and trust. Tools like cPanel often include settings to help you force HTTPS.
What is a Web Application Firewall (WAF) and why should I use one?
A WAF filters and monitors HTTP traffic between your web application and the internet, blocking threats and protecting your web server from malicious attacks. It works alongside SSL to ensure comprehensive security.
What is Domain Validation (DV)?
Domain Validation (DV) is a verification process to confirm domain ownership, a fundamental step in issuing most SSL certificates.
What is the difference between DV, OV, and EV certificates?
- DV (Domain Validation) certificates involve a simple verification of domain ownership.
- OV (Organization Validation) certificates provide additional verification of the organization’s identity.
- EV (Extended Validation) certificates offer the highest level of trust with rigorous verification processes.
What steps do I need to create secure configurations on my web server?
You need to set up automatic HTTPS redirects and integrate your SSL certificate with your web server’s security protocols, ensuring proper configuration for maintaining security and reliability. Using cPanel can simplify this process.
Why is authentication important in SSL certificate issuance?
Authentication ensures that the entity requesting the certificate is legitimate, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity and trustworthiness of encrypted communications.
What is the role of a CSR (Certificate Signing Request) in obtaining an SSL certificate?
A CSR is a block of encoded text generated on your server that contains information about your domain and public key, which is used by the Certificate Authority (CA) to issue your SSL certificate.
What is a self-signed SSL certificate, and should I use one?
A self-signed SSL certificate is one that you create yourself rather than obtaining from a trusted Certificate Authority. It can be used for internal purposes but is not recommended for public websites due to lack of trust by browsers.
What is Universal SSL?
Universal SSL is a feature offered by some providers like Cloudflare, which automatically provides SSL encryption for all websites under their management, making it easier to secure your site.
How can I handle insecure content and content errors when moving to HTTPS?
To avoid insecure content errors, ensure all resources (like images, scripts, and stylesheets) are loaded over HTTPS. Tools like the Really Simple SSL plugin can help fix mixed content issues.
Why do I need to secure the root domain and subdomains?
Securing the root domain and subdomains ensures comprehensive protection across your entire site, preventing security gaps that could be exploited.
Key Takeaways:
- An SSL certificate is essential for securing data exchanged between your website and its visitors.
- Google recommends SSL for all websites, rewarding secure sites with better search engine rankings.
- SSL certificates can be obtained for free through Let’s Encrypt, supported by many major hosting providers.
- Major browsers like Chrome and Firefox indicate a site’s security status with a padlock icon or warnings.
- Using the Really Simple SSL plugin simplifies the process of enabling HTTPS on your WordPress site.
- Ensuring HTTPS is enabled helps build trust with your visitors and improves your site’s performance.
- Always update Google Search Console and Google Analytics when migrating from HTTP to HTTPS.
We hope this guide helped you get a free SSL certificate for your WordPress site and understand more about how SSL certificates work.
Thanks to the free SSL certificate from Let’s Encrypt and the Really Simple SSL plugin it’s easier than ever to switch your WordPress site to HTTPS. Your visitors will feel confident browsing your site safely and you’ll benefit from slightly higher search rankings.
Have you made the switch to HTTPS? Let us know in the comments below.


0 Comments
Join in. The comments are closed after 30 days.